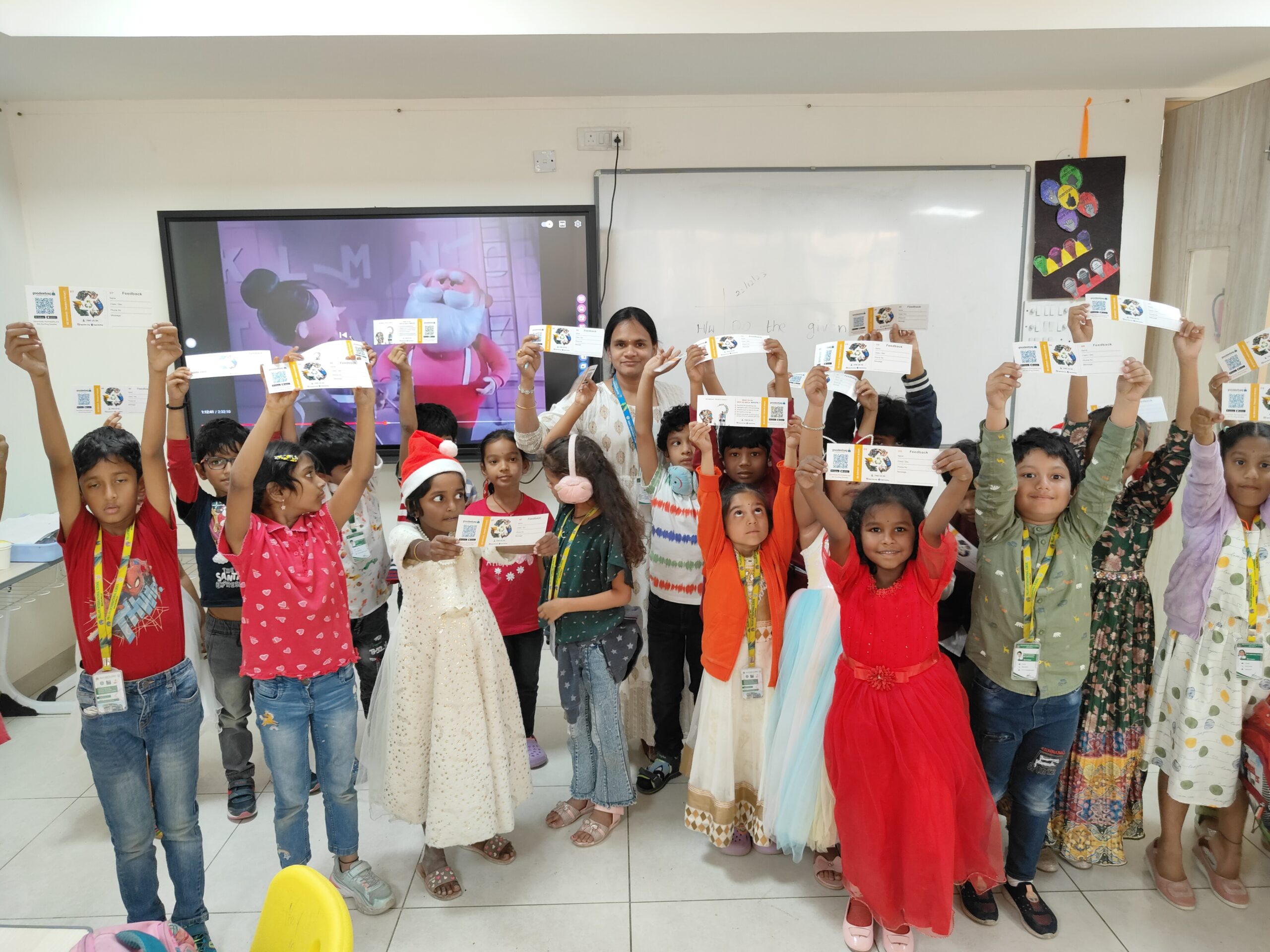
- T-hub , 1/c,83/1 ,Raidurg Panmaktha, Hyderabad | INDIA
Plastic Waste:
Its Impact on the Ocean, Animals, and the Environment
As humans, we generate about 57 lac 94 thousand 557 crore kilos of waste during our life time. Plastic and dry waste pollution pose severe threats to animals and the ocean. Marine life, such as sea turtles and seabirds, often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion that results in internal injuries, digestive issues, and malnutrition.
Entanglement in discarded fishing nets and plastic items is another distressing consequence for both marine and terrestrial animals, causing physical harm and sometimes leading to drowning. Additionally, plastics can absorb and accumulate toxic substances from the environment, leading to bioaccumulation and threatening the overall health of ecosystems.
In the ocean, plastic accumulates in large gyres, disrupting marine habitats, altering ocean circulation patterns, and contributing to the economic challenges faced by fisheries. The aesthetic degradation of coastlines and negative impacts on tourism further highlight the urgent need for comprehensive solutions to address this pervasive environmental problem.
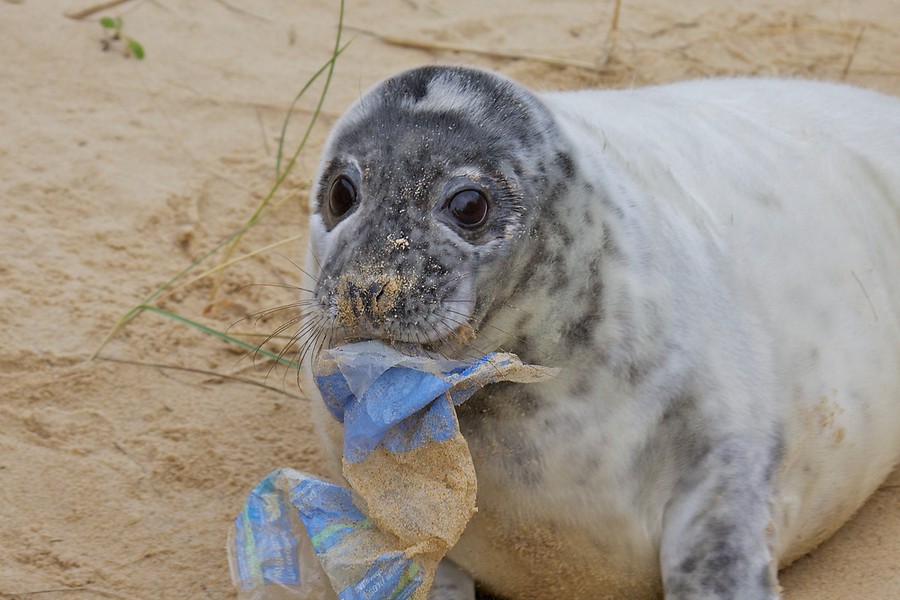
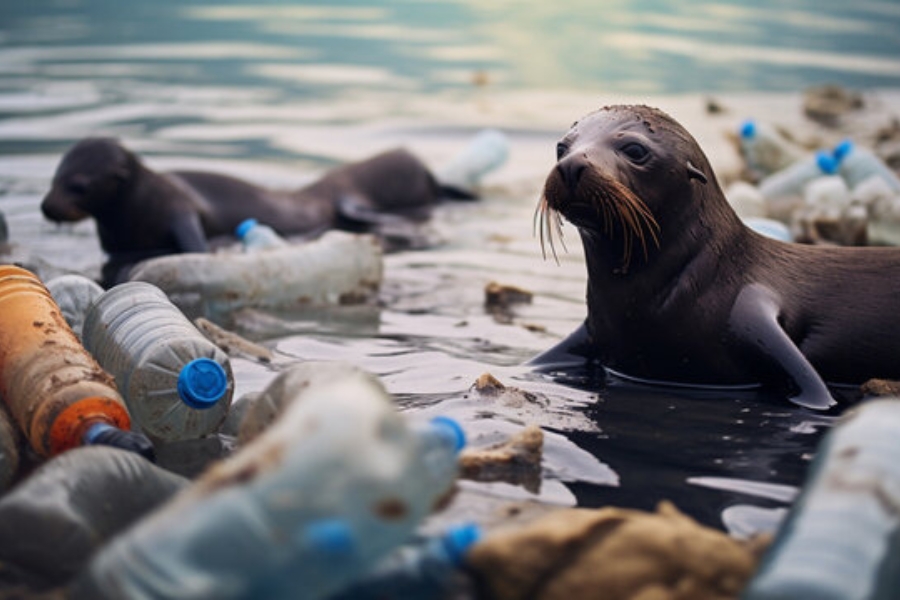






Impact on the Ocean:
The ocean serves as a vital life support system for our planet, regulating climate, providing food and livelihoods for millions of people, and harboring an incredible diversity of marine species.
Ingestion: Many marine animals mistake plastic pieces for food. Ingesting plastic can lead to internal injuries, digestive problems, and malnutrition. Sea turtles, whales, and seabirds are particularly vulnerable.
Entanglement: Animals may become entangled in discarded fishing nets, plastic bags, and other debris. This can hinder their movement, cause injuries, and lead to drowning.
Microplastics: Microplastics, resulting from the breakdown of larger plastic items, are consumed by filter-feeding organisms, entering the food chain and potentially affecting the health of various species.
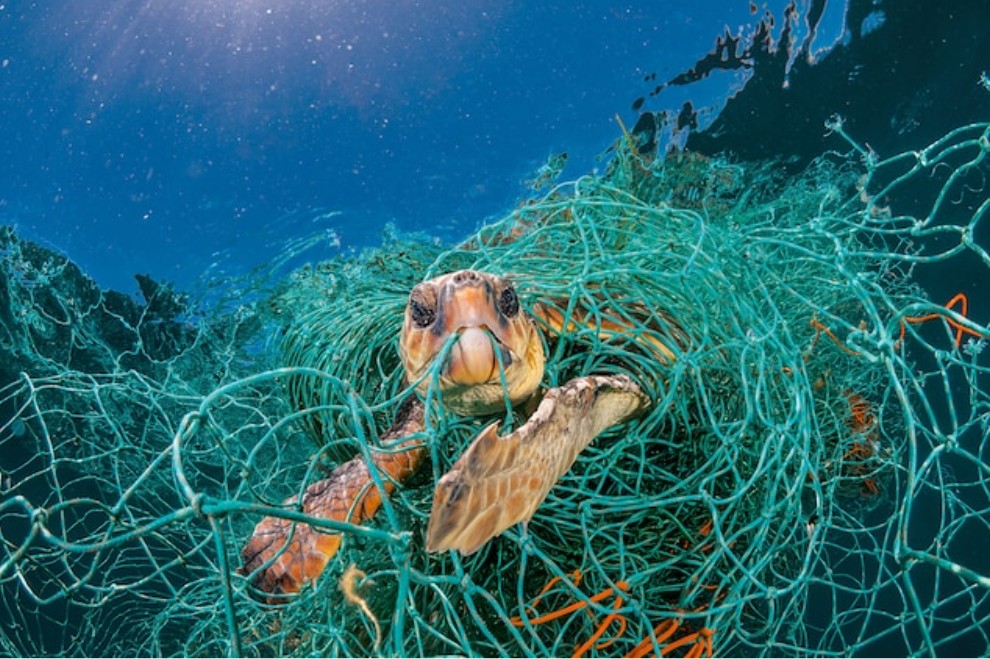
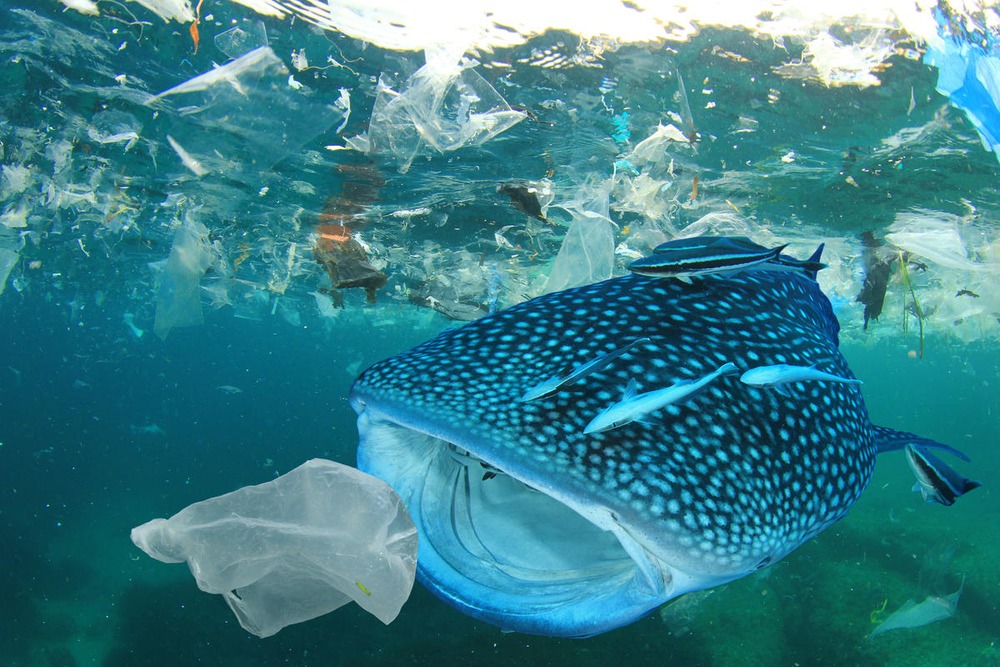
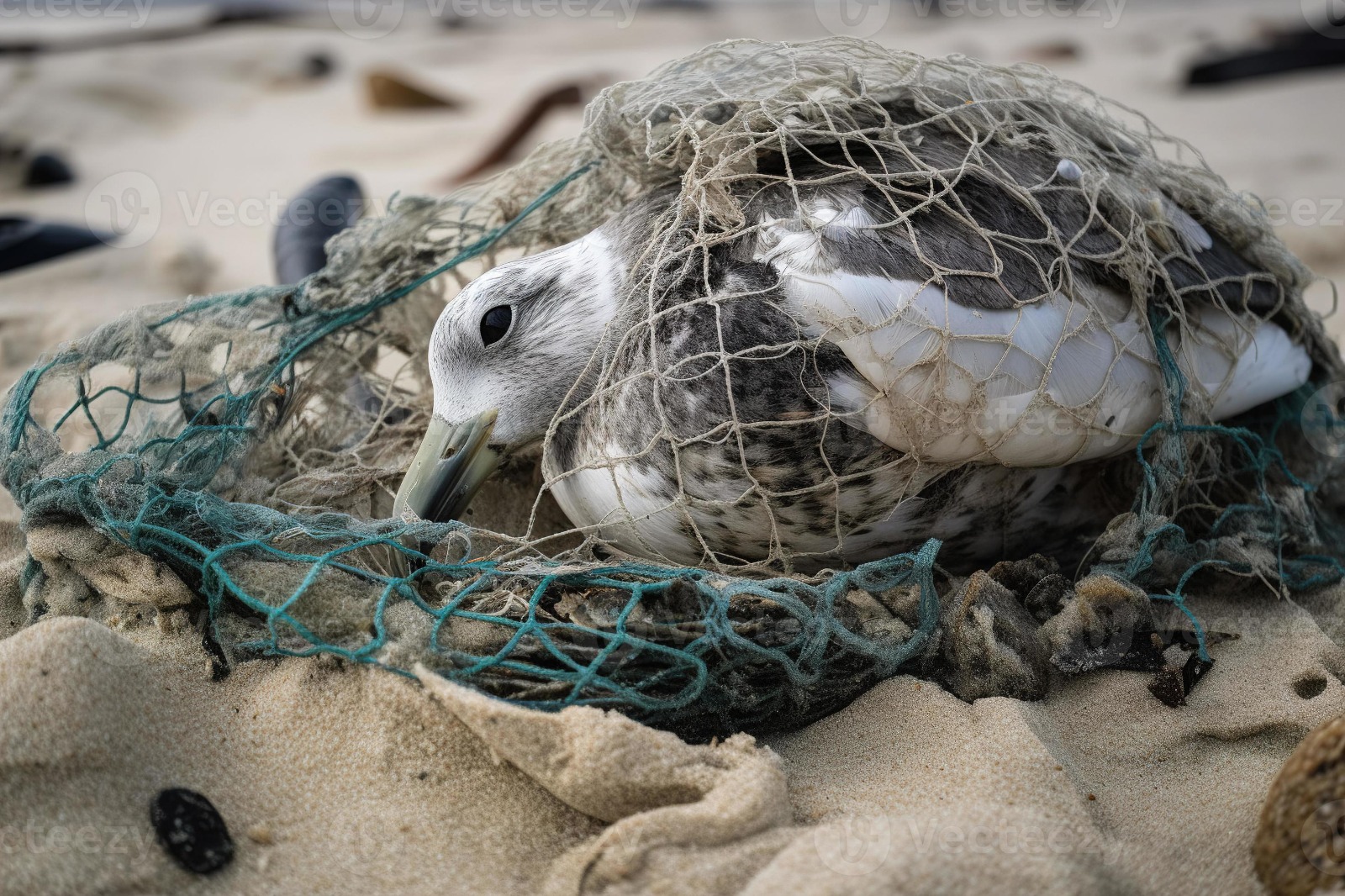
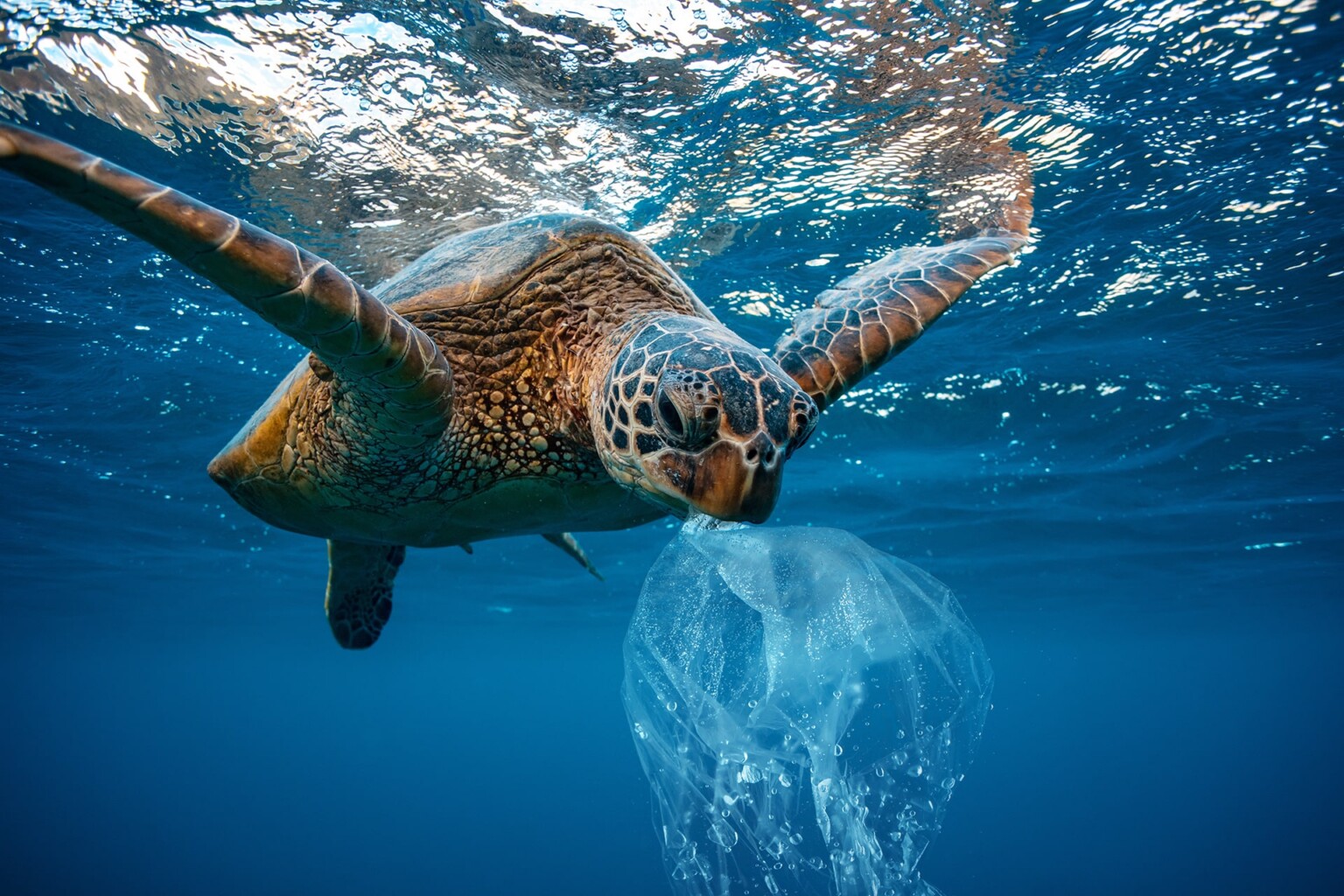




Toxicity: Plastics can absorb and accumulate toxins from the surrounding environment. When animals consume these plastics, they may also ingest concentrated toxic substances, leading to health issues and affecting entire ecosystems.
Water Quality: Plastics release harmful chemicals as they break down. These chemicals can leach into the water, negatively impacting the quality and health of marine environments.
Ecosystem Disruption: Plastic pollution alters marine ecosystems, affecting habitats such as coral reefs and seagrass beds. This, in turn, disrupts the balance of marine life and can lead to biodiversity loss.
Impact on Animals:
Plastic pollution poses a direct threat to marine and terrestrial animals alike. Seabirds, for example, are known to ingest large quantities of plastic debris, often mistaking it for food.
Furthermore, microplastics – tiny plastic particles less than 5 millimeters in size – have permeated the food chain, accumulating in the tissues of marine organisms. As predators consume contaminated prey, the concentration of plastic toxins magnifies, posing potential health risks to animals and humans alike.


Goodeebag is proudly powered by WordPress